Photo from wikipedia
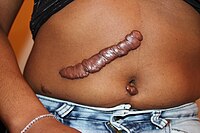
The abdominal skin is not a common area for keloid formation. The knowledge of laparoscopically induced keloids (LIK) remains little. This article aimed to review the case series of LIK… Click to show full abstract
The abdominal skin is not a common area for keloid formation. The knowledge of laparoscopically induced keloids (LIK) remains little. This article aimed to review the case series of LIK and analyse the characteristics. A retrospective and descriptive study was conducted. Patients' clinical records in the database were collected, including the demographics, medical history, laparoscopic surgery information, keloid information, and the severity of LIKs recorded using the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale. Twenty‐four LIK patients were enrolled. 18 patients were female and 10 had chronic diseases. 11 patients had non‐LIKs. 91.6% patients received laparoscopic cholecystectomy. LIKs were mainly located under the xiphoid process (N = 20), followed by the umbilicus (N = 16). 41.7% patients developed keloids at all trocha sites. The severity of the LIK was significantly negatively associated with the presence of the non‐LIK. Laparoscopic procedures could lead to the formation of keloids. Two types of LIKs were noticed: extended incisions induced long “spreading” type and trocha induced round bulging type. The presence of non‐LIKs could significantly reduce the severity of LIKs.
Journal Title: International Wound Journal
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!