Photo from wikipedia
Bipolaris oryzae causes rice brown spot (RBS) in common rice (Oryza sativa) inflicting substantial grain yield losses worldwide. Knowledge of the population structure, genetic diversity, and sexual recombination of the… Click to show full abstract
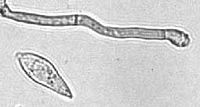
Bipolaris oryzae causes rice brown spot (RBS) in common rice (Oryza sativa) inflicting substantial grain yield losses worldwide. Knowledge of the population structure, genetic diversity, and sexual recombination of the fungal pathogen can help to implement effective disease management strategies. In this study, B. oryzae isolates sampled from Iran, The Philippines, and Japan were analyzed with 12 simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers newly developed from the genome sequence of the fungus. Among the 288 B. oryzae isolates genotyped, 278 unique haplotypes were identified. High genotype numbers (richness) with even distribution (evenness) were found within the collection sites. Both mating types, MAT1-1 and MAT1-2, were present in each collection area, and the sexual state was induced under controlled conditions with production of viable ascospores. However, the tests of linkage disequilibrium did allow rejection of the hypothesis of random mating. Discriminant analysis of principal components (DAPC) revealed that the B. oryzae collection formed three clusters each consisting of isolates from different collection sites. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed that genetic variation among clusters was 18.7%, with the rest distributed within clusters (Rst = 0.187, P < 0.001). Statistically significant pairwise-genetic differentiation was found between the clusters. These results show that Asian B. oryzae isolates are genetically diverse, and overall distributed in three groups. Those findings will be helpful in managing the disease and guide the use of representative set of isolates needed for selection of RBS resistant rice varieties. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Journal Title: Plant Pathology
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!