Photo from wikipedia
In this issue, Zhang et al report that a short course of low-dose IL-2 improved patients with polymyositis or dermatomyositis. This adds to the list of diseases for which efficacy… Click to show full abstract
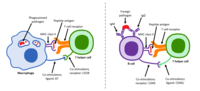
In this issue, Zhang et al report that a short course of low-dose IL-2 improved patients with polymyositis or dermatomyositis. This adds to the list of diseases for which efficacy of low-dose IL-2 has been reported.1 This is in line with the main activity of low-dose IL-2, the stimulation and expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs).1 Tregs are key to maintaining immune homeostasis. They control inflammation and the activation of effector T cells with autoimmune potential.2 Their depletion immediately unleashes major activation of effector T cells leading to fatal inflammation and the attack of otherwise healthy tissues, leading to multiorgan autoimmunity.3 This observation indicates that, at homeostasis, there is a balance between Tregs and effector T cells that prevents severe inflammation and autoimmunity. This, in turn, teaches us that any chronic breach of this homeostasis, that is, an autoimmune condition, inherently signals Treg insufficiency.1 Such Treg insufficiency does not imply a Treg deficiency, but reflects …
Journal Title: Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!