Photo from wikipedia
Strongyloidiasis is a disease caused by the intestinal helminth Strongyloides stercoralis. When the immune system of infected individuals is compromised, larvae may migrate from the gastrointestinal tract to other tissues,… Click to show full abstract
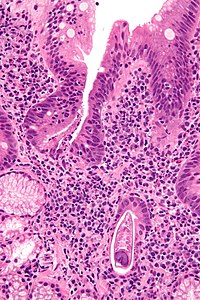
Strongyloidiasis is a disease caused by the intestinal helminth Strongyloides stercoralis. When the immune system of infected individuals is compromised, larvae may migrate from the gastrointestinal tract to other tissues, causing S. stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome, which has a reported mortality of 71%. In this case, we report a patient with S. stercoralis hyperinfection syndrome with central nervous system (CNS) involvement. An elderly South East Asian male tourist presented with pulmonary symptoms, fever and infiltrates on chest X-ray. He later developed symptoms of CNS infection. S. stercoralis larvae were found in a stool sample. Microbiological examination of cerebrospinal fluid revealed S. stercoralis-specific DNA. The patient was treated with oral and rectal ivermectin and albendazole. The condition was complicated by sepsis, bacteraemia and hypereosinophilia. Unfortunately, the patient eventually died from pulmonary oedema and insufficiency. This case highlights the global importance of Strongyloides CNS infection in endemic and non-endemic regions.
Journal Title: BMJ Case Reports
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!