Photo from wikipedia
Introduction The optimal management of pneumothorax remains undefined. There is a growing consensus that patients with spontaneous pneumothorax can be considered for ambulatory management with the use of a one-way… Click to show full abstract
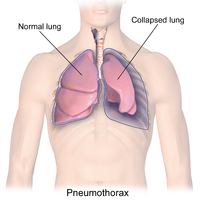
Introduction The optimal management of pneumothorax remains undefined. There is a growing consensus that patients with spontaneous pneumothorax can be considered for ambulatory management with the use of a one-way valve. Despite this, there is little data on the outcomes of outpatient management of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP). Methods At our institution, selected patients with primary and secondary spontaneous pneumothorax who meet the predefined local criteria are managed on an ambulatory pathway. We prospectively evaluated our practice over a 3-year period and explore outcomes of patients with SSP using primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP) as a comparator group. Results 163 consecutive patients presenting to our hospital between September 2014 and July 2017 were evaluated using a predefined protocol. 111 (49 SSP and 62 PSP) were deemed suitable for outpatient management. Resolution on day 5 was similar between the two groups (65% in the SSP vs 79% in the PSP group; p=0.108). The mean drainage time was 5.84 days in SSP compared with 5.69 days in PSP, representing a difference of 0.15 days (95% CI −2.47 to 2.16; p=0.897). Complications such as infection and drain blockage/falling-out were scarce, with comparable pain and satisfaction scores across both groups. There were no deaths during this period. An estimated £86 796 ($113 920) was saved over the study period, equating to £1118.80 ($1550) per patient. Discussion This study suggests that outpatient management of selected patients with SSP may be effective, safe and cost-saving.
Journal Title: BMJ Open Respiratory Research
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!