Photo from wikipedia
World War 1 ended 100 years ago. The aftermath included the consolidation of significant advances in medical care of casualties. Some of these advances were made in the care of… Click to show full abstract
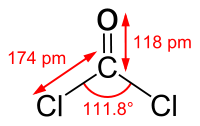
World War 1 ended 100 years ago. The aftermath included the consolidation of significant advances in medical care of casualties. Some of these advances were made in the care of chemical casualties, in particular the mechanisms of toxicity and treatment of phosgene exposure. Phosgene, or carbonyl chloride, is an extremely poisonous vapour that was used to devastating effect during World War 1. Observations made of acutely poisoned casualties formed the basis of much research in the early post-World War 1 era. Some extremely elegant experiments, some at the nascent Porton Down research facility, further evaluated the toxin and defences against it. Researchers drew on knowledge that was later forgotten and has since been relearnt later in the 20th century and made many correct assumptions. Their work is the bedrock of our understanding of phosgene toxicity that survives to this day. The horrors of chemical warfare prompted the Geneva Protocol of 1925, prohibiting the use of chemical agents in warfare, and chemical warfare on this scale has not been repeated. The ease with which phosgene can be synthesised requires healthcare providers to be familiar with its effects.
Journal Title: Journal of the Royal Army Medical Corps
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!