Photo from wikipedia
BACKGROUND To investigate the role of psychological factors (anxiety and depression) and pain measured on a visual analogue scale (VAS) in the development of complex regional pain syndrome type I… Click to show full abstract
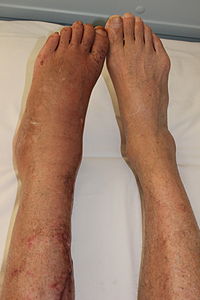
BACKGROUND To investigate the role of psychological factors (anxiety and depression) and pain measured on a visual analogue scale (VAS) in the development of complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I) following the distal radius fracture (DRF). METHODS A consecutive sample of patients (N=60) with a distal radius fracture was measured for signs of CRPS by Budapest criteria weekly till 8 weeks and then another follow-up one year after injury to determine the incidence and predictors of developing CRPS I in a prospective cohort study and also to discover whether there is difference between pain, depression, and anxiety level in the patients with and without CRPS I. The most of the patients were treated by Pin stabilization. The Beck depression inventoryshort form (BDI), State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, and Numerical pain rating scale were used to determine the patients' psychological features and pain intensity at the base line and 8 weeks after the fracture. RESULTS CRPS I developed in 15 (25%) patients after eight weeks and just last in 10 (16.67%) patients after one year. No difference was found between the two groups (CRPS and non-CRPS group) in terms of state (STAI-I) and trait (STAI-II) anxiety, and BDI score. Pain at the base line was the most important risk factor in developing CRPS (odds ratio [OR] =1.52; 95% CI). CONCLUSIONS After fracturing the distal radius, patients who have high pain intensity have a higher risk of developing CRPS I. To following these patients closely for the development of CRPS I may be advantageous for early preventative and therapeutic interventions.
Journal Title: The journal of hand surgery Asian-Pacific volume
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!