Photo from wikipedia
Background: Postoperative evaluation of wrist joint trauma is divided into patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and clinician-reported outcomes (CROs). We investigated the association of the Q-DASH score as the postoperative PROs and… Click to show full abstract
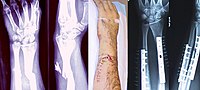
Background: Postoperative evaluation of wrist joint trauma is divided into patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and clinician-reported outcomes (CROs). We investigated the association of the Q-DASH score as the postoperative PROs and the Mayo wrist score as the postoperative CROs with clinical evaluation in patients with distal radius fractures surgically treated using a volar locking plate (VLP). Moreover, whether PROs and CROs are correlated to the clinical evaluation was investigated. Methods: The subjects were 109 patients surgically treated for distal radius fractures at our hospital between June 2013 and May 2017. Forty-one patients were male, 68 patients were female, and the mean age was 61.4 (19-86) years old. The fracture type was AO classification A type in 30 patients (A2: 25, A3: 5), B type in 5 (B2: 1, B3: 4), and C type in 74 (C1: 50, C2: 11, C3: 13). All patients were surgically treated using VLP. The range of motion of the wrist, grip strength the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), the Q-DASH score (PROs), and the Mayo wrist score (CROs) were investigated. Each evaluation was compared as the clinical outcome between at 3 months after surgery and the final follow-up. In addition, the correlations of the postoperative PROs and CROs with the clinical evaluation were analyzed. Results: Each evaluation was significantly improved compared with that at 3 months after surgery. There was a significant correlation between PROs and CROs at 3 months after surgery and the final follow-up. However, the range of motion of the wrists was not significantly correlated with PROs or CROs at 3 months after surgery or at the final follow-up. Conclusions: On evaluation after surgery for distal radius fractures, PROs and CROs improved early after surgery (3 months after surgery) before the final follow-up, and an inverse correlation was present between these scores.
Journal Title: The journal of hand surgery Asian-Pacific volume
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!