Photo from wikipedia
Competence refers to the specialized physiological state in which bacteria undergo transformation through the internalization of exogenous DNA in a controlled and genetically encoded process that leads to genotypic and,… Click to show full abstract
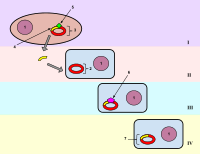
Competence refers to the specialized physiological state in which bacteria undergo transformation through the internalization of exogenous DNA in a controlled and genetically encoded process that leads to genotypic and, in many cases, phenotypic changes. Natural transformation was first described in Streptococcus pneumoniae and has since been demonstrated in numerous species, including Bacillus subtilis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Homologs of the genes encoding the DNA uptake machinery for natural transformation have been reported to be present in several lactic acid bacteria, including Lactobacillus spp., Streptococcus thermophilus, and Lactococcus spp. In this review, we collate current knowledge of the phenomenon of natural transformation in Gram-positive bacteria. Furthermore, we describe the mechanism of competence development and its regulation in model bacterial species. We highlight the importance and opportunities for the application of these findings in the context of bacterial starter cultures associated with food fermentations as well as current limitations in this area of research.
Journal Title: Annual review of food science and technology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!