Photo from wikipedia
Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) is part of a larger clinicopathological entity, venous thromboembolism. It is also a complex, multifactorial disorder divided into four major disease processes including venous thrombosis, thrombus in… Click to show full abstract
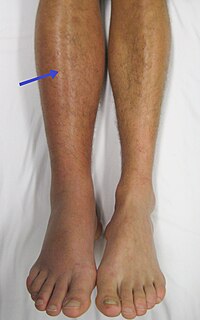
Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) is part of a larger clinicopathological entity, venous thromboembolism. It is also a complex, multifactorial disorder divided into four major disease processes including venous thrombosis, thrombus in transit, acute pulmonary embolism, and pulmonary circulation reconstruction. Even when treated, some patients develop chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. PTE is also a common fatal type of pulmonary vascular disease worldwide, but earlier studies primarily focused on the pathological changes in the blood component of the disease. With contemporary advances in molecular and cellular biology, people are becoming increasingly aware of coagulation pathways, the function of vascular smooth muscle cells, microparticles, and the inflammatory pathways that play key roles in PTE. Combined hypoxia and immune research has revealed that PTE should be regarded as a class of complex diseases caused by multiple factors involving the vascular microenvironment and vascular cell dysfunction.
Journal Title: BioMed Research International
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!