Photo from wikipedia
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a serious hematological tumor derived from early T-cell progenitors, which is extremely resistant to chemotherapy. Classically, doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective first-line drug for… Click to show full abstract
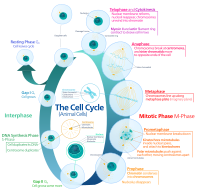
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a serious hematological tumor derived from early T-cell progenitors, which is extremely resistant to chemotherapy. Classically, doxorubicin (DOX) is an effective first-line drug for the treatment of T-ALL; however, DOX resistance limits its clinical effect. The DEK proto-oncogene (DEK) has been involved in neoplasms but remains unexplored in T-ALL. We silenced DEK on Jurkat cells and detected cell proliferation with cell counting and colony formation assay. Then, we detected DEK's drug sensitivity to DOX with CCK-8, cell cycle, and apoptosis with DOX treatment. Western blot analysis was performed to determine protein expression of apoptosis and cell cycle-related genes, including BCL2L1, caspase-3, and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK). Finally, the tumorigenic ability of DEK was analyzed using a BALB/C nude mouse model. In this study, DEK was highly expressed in Jurkat cells. Inhibition of DEK can lead to decreased cell proliferation and proportion of S-phase cells in the cell cycle and more cell apoptosis, and the effect is more obvious after DOX treatment. Western blot results showed that DOX treatment leads to cell cycle arrest, reduction of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) protein, accumulation of CDKN1A protein, and DOX-induced apoptosis accompanied by reductions in protein levels of BCL2L1, as well as increases in protein level of caspase-3. Furthermore, DEK-silenced Jurkat cells generated a significantly smaller tumor mass in mice. Our study found that DEK is a novel, potential therapeutic target for overcoming DOX resistance in T-ALL.
Journal Title: Disease Markers
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!