Photo from wikipedia
Background Exercise training (ET) is current treatment method for venous insufficiency (VI). The comprehensive effect of ET in addition to compression therapy (CT) in VI is not clear. Method Twenty-four… Click to show full abstract
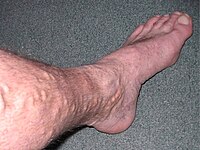
Background Exercise training (ET) is current treatment method for venous insufficiency (VI). The comprehensive effect of ET in addition to compression therapy (CT) in VI is not clear. Method Twenty-four patients with VI were randomly divided into exercise group (EG) and control group (CG). While CG received only CT, EG was applied ET consisting of aerobic, strengthening and stretching exercises in addition to CT for 2 days/week, 6 weeks at hospital under the supervision of physiotherapist. All the patients were assessed with Chronic Venous Disease Quality Of Life Questionnaire-20, Short Form-36, Duplex Doppler Ultrasonography, Venous Clinical Severity Score, hand-held dynamometer, Visual Analogue Scale, circumference measurements, 6 minute-walking test, and 10-meter-walking test before and after the treatment. Result Except of hemodynamic status and edema (p > 0.05), all parameters were significantly different in favor of EG (p < 0.05). Conclusion ET in addition to CT was more effective and safe treatment in VI.
Journal Title: Phlebology
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!