Photo from wikipedia
Pediatric chronic myelogenous leukemia is uncommon. We report a pediatric patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia presenting with a normal white blood cell count and no circulating immature myeloid cells. The… Click to show full abstract
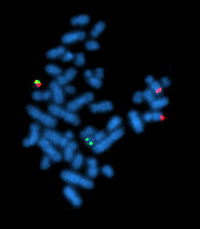
Pediatric chronic myelogenous leukemia is uncommon. We report a pediatric patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia presenting with a normal white blood cell count and no circulating immature myeloid cells. The patient presented with extreme thrombocytosis (platelet count range: 2175–3064 × 109/L) noted incidentally. No splenomegaly was found. Examination of the bone marrow aspirate revealed normal cellularity and normal myeloid: erythroid ratio with marked megakaryocytic hyperplasia. Molecular studies on the bone marrow aspirate detected both the major BCR/ABL1 p210 fusion transcript (9280 copies; p210/ABL1 ratio: 38.2%) and the minor p190 transcript (below limit of quantitation). The platelet count normalized within 2 weeks after treatment with the second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib. Follow-up after 3 months revealed a 1.87 log reduction in p210 transcripts compared to diagnosis and no detectable p190 transcripts. This case highlights the need to include BCR/ABL1 fusion testing to accurately diagnose pediatric patients presenting with isolated thrombocytosis.
Journal Title: Pediatric and Developmental Pathology
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!