Photo from wikipedia
Background Surgical excision is considered standard treatment for nodular basal cell carcinoma (nBCC). However, patients who reject or are unsuited for surgery may benefit from imiquimod (IMQ) 5% cream as… Click to show full abstract
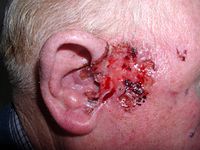
Background Surgical excision is considered standard treatment for nodular basal cell carcinoma (nBCC). However, patients who reject or are unsuited for surgery may benefit from imiquimod (IMQ) 5% cream as an alternative treatment. Objectives The objective of this study was to conduct a systematic review on the efficacy and safety of IMQ for the treatment of nBCC. Materials and Methods The terms basal cell carcinoma AND imiquimod OR Aldara were searched on Ovid-MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases. Articles were included if they reported the efficacy or side effects of IMQ for nBCC. Primary outcomes included clearance (clinical and histological), recurrence rates, and adverse events. Number of lesions/subjects, treatment regimens, length of treatment, and time to recurrence were secondary outcomes. Results Thirty-nine publications, totaling 738 lesions, revealed a 77.4% (335/433 lesions) clinical and 72.9% (390/535 lesions) histological clearance rate. Regimens ranged from once daily 2 days a week to twice daily 7 days a week. Average treatment duration was 8.81 (±3.49) weeks. There was a 1.80% recurrence rate after an average follow-up period of 13.03 (±15.09) months. Common adverse effects included erythema (77.2%), crusting (50.5%), pruritus (34.1%), tenderness/irritation (27.3%), ulceration (25.4%), burning (22.1%), and erosion (21.7%). Unforeseen side effects included conjunctivitis, keratitis, depigmentation, comedone formation, and ruptured epidermoid cysts. Conclusion Imiquimod showed clinical and histological clearance rates of over 70% for nBCC, with a recurrence rate of 1.80%. Although clearance rates are lower than surgery, IMQ can be considered as a treatment option for nBCC in those who decline or are unfit for surgical intervention.
Journal Title: Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!