Photo from wikipedia
Background: Giant cell tumors (GCTs) of the distal ulna are rare. Despite being benign, they can be locally aggressive and may recur following conventional treatment by curettage and bone grafting.… Click to show full abstract
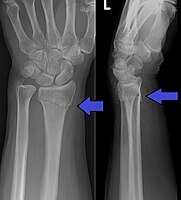
Background: Giant cell tumors (GCTs) of the distal ulna are rare. Despite being benign, they can be locally aggressive and may recur following conventional treatment by curettage and bone grafting. Salvage reconstructive options after failed conventional treatment include Darrach resection, Suave-Kapandji procedure, hemi-arthroplasty, or total joint arthroplasty. Methods: We discuss reconstruction options for the distal radio-ulnar joint following tumor resection, and present the outcomes of a constrained distal radio-ulnar prosthesis in a 29-year-old male following resection of a distal ulna GCT. Results: Reconstruction of the distal radio-ulnar joint by a constrained prothesis yielded excellent functional outcomes following resection of a GCT of the distal ulna. Conclusions: This case demonstrates that successful oncologic and functional outcomes can be achieved by radical resection of a recurrent GCT of the distal ulna and reconstruction with a constrained total joint arthroplasty.
Journal Title: HAND
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!