Photo from wikipedia
Background Tracheal intubation is the gold standard in emergency airway management. One way of measuring intubation quality is first pass success rate (FPSR). Mastery of tracheal intubation and maintenance of… Click to show full abstract
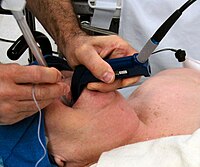
Background Tracheal intubation is the gold standard in emergency airway management. One way of measuring intubation quality is first pass success rate (FPSR). Mastery of tracheal intubation and maintenance of the skill is challenging for non-anesthesiologists. A combination of individual measures can increase FPSR. Videolaryngoscopy is an important tool augmenting laryngeal visualization. Bougie-first strategy can further improve FPSR in difficult airways. Standardized positioning maneuvers and manipulation of the soft tissues can enhance laryngeal visualization. Fresh frozen cadavers (FFC) are superior models compared to commercially manufactured manikins. By purposefully manipulating FFCs, it is possible to mimic the pre-hospital intubation conditions of helicopter emergency medical service (HEMS). Methods Twenty-four trauma surgeons (12 per Group, NOVICES: no pre-hospital experience, HEMS: HEMS physicians) completed an airway training course using FFCs. The FFCs were modified to match airway characteristics of 60 prospectively documented intubations by HEMS physicians prior to the study (BASELINE). In four scenarios the local HEMS airway standard (1: unaided direct laryngoscopy (DL), OLD) was compared to two scenarios with modifications of the intubation technique (2: augmented DL (bougie and patient positioning), 3: augmented videolaryngoscopy (aVL)) and a control scenario (4: VL and bougie, positioning by participant, CONTROL). FPSR, POGO score, Cormack and Lehane grade and duration of intubation were recorded. No participant had anesthesiological qualifications or experience in VL. Results The comparison between CONTROL and BASELINE revealed a significant increase of FPSR and achieved C&L grade for HEMS group (FPSR 100%, absolute difference 23%, p ≤ .001). The use of videolaryngoscopy, bougie, and the application of positioning techniques required significantly more time in the CONTROL scenario (HEMS group: mean 34.0 s (IQR 28.3–47.5), absolute difference to BASELINE: 13.0 s, p = .045). The groups differed significantly in the median number of real-life intubations performed in any setting (NOVICES n = 5 (IQR 0–18.75), HEMS n = 68 (IQR 37.25–99.75)). In the control scenario no significant differences were found between both groups. The airway characteristics of the FFC showed no significant differences compared to BASELINE. Conclusion Airway characteristics of a pre-hospital patient reference group cared for by HEMS were successfully reproduced in a fresh frozen cadaver model. In this setting, a combination of evidence based airway management techniques results in high FPSR and POGO rates of non-anesthesiological trained users. Comparable results (FPSR, POGO, duration of intubation) were achieved regardless of previous provider experience. The BOAH concept can therefore be used in the early stages of airway training and for skill maintenance.
Journal Title: Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!