Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Purpose The main objective of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the clinical and radiological outcomes of acute (AMF) and chronic Monteggia fractures (CMF) in children treated by closed… Click to show full abstract
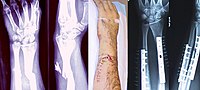
Abstract Purpose The main objective of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the clinical and radiological outcomes of acute (AMF) and chronic Monteggia fractures (CMF) in children treated by closed or open reduction and external fixation (EF). Methods This is a retrospective review of 26 patients with Monteggia fracture. Patients with AMF (time between trauma and surgery less than two weeks) were treated by closed reduction and EF of the ulna (Group A; 15 patients) while those with CMF (time between trauma and surgery more than three weeks) were managed by closed or open reduction and EF of the ulna (Group B; 11 patients). Clinical outcome was evaluated with radiography and the short version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand outcome questionnaire (Quick DASH). Complications were recorded in both groups. Results No secondary displacement, wire migration, consolidation delays, nonunion, malunion or re-fracture was noted. However, one patient in Group A (6.7%) developed heterotopic ossification of the ulna; the final functional outcome was good (Quick DASH score: 18.2). One case of postoperative redislocation of the radial head was detected in Group B (9.1%). Two patients (7.6%) developed transient pin tract infection. Despite the fact that 16 out of 26 patients (six in Group A and ten in Group B) complained of the clinical appearance and/or had intermittent residual pain on the injured side, the results were essentially the same between the two groups of patients (p > 0.05). Conclusion EF is an alternative for the management of acute and chronic paediatric Monteggia fractures. It provides satisfactory radiological and clinical outcomes with relatively low rates of complications. Level of evidence IV
Journal Title: Journal of Children's Orthopaedics
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!