Photo from wikipedia
A modal interferometer method (MIM) is applied to measure the differential mode delay (DMD) between the L P 0m modes traversing a step-index multimode fiber (SI-MMF). Only linearly polarized radial… Click to show full abstract
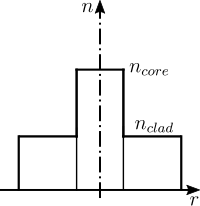
A modal interferometer method (MIM) is applied to measure the differential mode delay (DMD) between the L P 0m modes traversing a step-index multimode fiber (SI-MMF). Only linearly polarized radial modes, i.e., L P 0m modes, are excited and transmitted in the SI-MMF by using a single-mode-multimode-single-mode (SMS) fiber structure. The measurement principle is based on investigating a transmitted spectrum through temporal decomposition by means of a Fourier transform. The Fourier-transform-based MIM provides simultaneous measurements of the DMD between the L P 0m modes. The wavelength dependence of the DMD is estimated experimentally in both the 1260-1360 nm and 1450-1625 nm telecommunication bands. The normalized frequency dependence of the DMD is also investigated theoretically. The result suggests that the 1260-1360 nm band is preferable to the 1450-1625 nm band for a mode-division multiplexing (MDM) transmission employing an SI-MMF in terms of realizing a smaller DMD.
Journal Title: Applied optics
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!