Photo from wikipedia
Decidualization is a process of differentiation of human endometrial stromal cells (hESCs) accompanied by dramatic changes in cellular functions. This process is critical for embryo implantation and the establishment of… Click to show full abstract
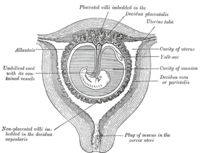
Decidualization is a process of differentiation of human endometrial stromal cells (hESCs) accompanied by dramatic changes in cellular functions. This process is critical for embryo implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. Impairment of decidualization of hESCs leads to implantation failure, miscarriage, and unexplained infertility. The present review focuses on the metabolic changes in hESCs during decidualization. One of the changes taking place is in the glucose metabolism. Glucose uptake increases during decidualization because glucose is essential for the decidualization of hESCs. In hESCs, GLUT1 is highly expressed and involved in the increase of glucose uptake during decidualization. The up-regulation of GLUT1 is mediated by an epigenetic mechanism, which is regulated by CCAAT enhancer-binding protein β (C/EBPβ) and Wilms tumor 1 (WT1). Another metabolic change is in the lipid metabolism. Lipid accumulation in hESCs increases during decidualization. This increase is mediated by very low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR). The up-regulation of VLDLR is regulated by WT1. In contrast to glucose, lipid is not essential for decidualization of hESCs. Endometrial cells have been implicated as important sources of nutrition for the embryo. hESCs may increase glucose and lipid storage so that they can supply them to the embryo during the implantation process. Taken together, decidualization is the process accompanied by metabolic changes, which may be associated with successful implantation.
Journal Title: Endocrine journal
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!