Photo from wikipedia
Abstract The maintenance of energy homeostasis is achieved with ‘detectors’ that receive signals from the external and internal environment and with multidirectional ‘communication routes’ including neuronal networks and body fluids,… Click to show full abstract
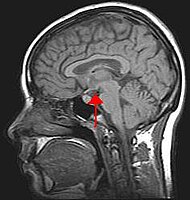
Abstract The maintenance of energy homeostasis is achieved with ‘detectors’ that receive signals from the external and internal environment and with multidirectional ‘communication routes’ including neuronal networks and body fluids, such as blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Changes in the energy demands of organisms are caused by current physiological status and environmental conditions, including season and food availability. Little is known about the interactions between the metabolic indicators involved in the maintenance of energy homeostasis, e.g., leptin, orexins and ghrelin. Sheep and other seasonal animals are highly adaptable to their environments because of the plasticity of their neural and endocrine systems. Sheep exhibit leptin resistance and are thus an extremely interesting model for research on the relationship between hormonal indicators of energy metabolism. The paper is focused mainly on the anatomical and functional communication between leptin, ghrelin and orexins, which play principal roles in the adaptation of energetic demands to environmental fluctuations.
Journal Title: Annals of Animal Science
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!