Photo from wikipedia
Epitranscriptomic modification of RNA regulates human development, health, and disease. The true diversity of the transcriptome in breast cancer including chemical modification of transcribed RNA (epitranscriptomics) is not well understood… Click to show full abstract
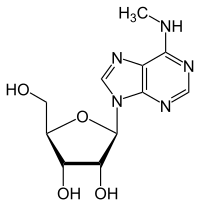
Epitranscriptomic modification of RNA regulates human development, health, and disease. The true diversity of the transcriptome in breast cancer including chemical modification of transcribed RNA (epitranscriptomics) is not well understood due to limitations of technology and bioinformatic analysis. N-6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant epitranscriptomic modification of mRNA and regulates splicing, stability, translation, and intracellular localization of transcripts depending on m6A association with reader RNA binding proteins. m6A methylation is catalyzed by the METTL3 complex and removed by the specific m6A demethylase ALKBH5, with FTO's role as an 'eraser' uncertain. In this review, we provide and overview of epitranscriptomics related to mRNA and focus on m6A in mRNA and its detection. We summarize current knowledge on altered levels of writers, readers, and erasers of m6A and their roles in breast cancer and association with prognosis. We summarize studies identifying m6A peaks and sties in genes in breast cancer cells.
Journal Title: Journal of molecular endocrinology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!