Photo from wikipedia
Hydatid cyst disease continues to be an important public problem today. The causative agent of this disease is a parasite belonging to the cestode class, Echinococcus granulosus1. Carnivorous animals are… Click to show full abstract
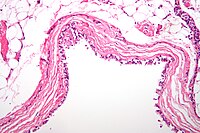
Hydatid cyst disease continues to be an important public problem today. The causative agent of this disease is a parasite belonging to the cestode class, Echinococcus granulosus1. Carnivorous animals are the parasite's definitive hosts, and the disease is transmitted via the fecal-oral route. The eggs of the tapeworm in the main host are excreted in feces. Water and food contaminated with these feces are taken up by intermediate hosts. The life cycle continues when carnivorous animals consume the cyst-containing internal organs of herbivorous intermediate hosts. Hydatid cysts grow faster in children than adults due to the elasticity of the lung2,3. Hydatid cysts may rarely cause a mediastinal shift. Children with pulmonary hydatid cysts should be treated surgically as soon as possible.
Journal Title: Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!