Photo from wikipedia
Caudal vena cava thrombosis (CVCT) is an acute disease secondary to ruminal lactic acidosis and rumenitis with fatal outcome in cattle fed with a high-grain diet. The aim of this… Click to show full abstract
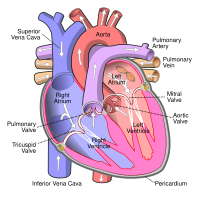
Caudal vena cava thrombosis (CVCT) is an acute disease secondary to ruminal lactic acidosis and rumenitis with fatal outcome in cattle fed with a high-grain diet. The aim of this paper is to describe CVCT in an adult Holstein cow from a herd in Balcarce, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Clinical signs included dyspnea, weakness, recumbence, and hemoptysis, followed by death in 3.5 days. Important necropsy findings included multiple hepatic abscesses, a septic thrombus (4.0cm x 2.0cm) in the vena cava adjacent to the liver, and a 15cm hematoma in the right lung. Histological lesions observed in the pulmonary parenchyma included suppurative pneumonia with embolic bacterial colonies and severe interstitial fibroplasia. Dissociation and degeneration of elastic fibers were observed in the pulmonary arteries, and necrotizing vasculitis was present in the caudal vena cava. We concluded that CVCT should be included in the differential diagnosis of diseases with acute respiratory signs. The preventive measures to control the CVCT include the reduction of lactic acidosis.
Journal Title: Ciencia Rural
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!