Photo from wikipedia
One of the most common referrals to the electrodiagnostic (EDX) laboratory is to confirm a clinical impression of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). The EDX studies are valuable in localizing median… Click to show full abstract
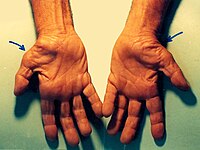
One of the most common referrals to the electrodiagnostic (EDX) laboratory is to confirm a clinical impression of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). The EDX studies are valuable in localizing median nerve abnormalities to the wrist, grading its severity, and excluding other condition that can mimic or coexist with CTS. However, there are many clinical and EDX pitfalls that can lead to misdiagnosis. Careful clinical assessment and attention to technical factors and details of the EDX techniques are fundamental for the quality and accurate interpretation of the study. This review aims to discuss the clinical and the EDX approaches to the diagnosis of CTS with emphasis on the commonly encountered pitfalls.
Journal Title: Neurosciences
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!