Photo from wikipedia
144Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting has become a promising approach to constructing functional biomimetic tissues for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. In 3D bioprinting, bio-inks are essential for the construction of cell… Click to show full abstract
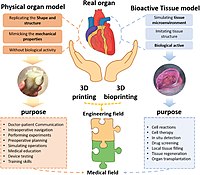
144Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting has become a promising approach to constructing functional biomimetic tissues for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. In 3D bioprinting, bio-inks are essential for the construction of cell microenvironment, thus affecting the biomimetic design and regenerative efficiency. Mechanical properties are one of the essential aspects of microenvironment, which can be characterized by matrix stiffness, viscoelasticity, topography, and dynamic mechanical stimulation. With the recent advances in functional biomaterials, various engineered bio-inks have realized the possibility of engineering cell mechanical microenvironment in vivo. In this review, we summarize the critical mechanical cues of cell microenvironments, review the engineered bio-inks while focusing on the selection principles for constructing cell mechanical microenvironments, and discuss the challenges facing this field and the possible solutions for them.
Journal Title: International Journal of Bioprinting
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!