Photo from wikipedia
AIM To present the clinical manifestations of 5 autosomal dominant cone-rod dystrophy (adCORD) patients from two Chinese families with cone-rod homeobox (CRX) mutation (p.R41W), and to explore the clinical heterogeneity… Click to show full abstract
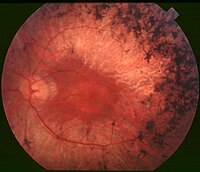
AIM To present the clinical manifestations of 5 autosomal dominant cone-rod dystrophy (adCORD) patients from two Chinese families with cone-rod homeobox (CRX) mutation (p.R41W), and to explore the clinical heterogeneity of adCORD with CRX mutation (p.R41W). METHODS Interrogation and ophthalmological examinations were undertaken in all patients and unaffected members. Analysis of clinical features was performed by visual acuity, slit lamp examination, visual field examination, fundoscopy, autofluorescence and spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Targeted next-generation sequencing was applied as a useful tool to identify the causative mutation of CORD genes. RESULTS A CRX missense mutation c.121C>T was identified in all patients, resulting in an amino acid change from arginine acid to tryptophan (p.R41W). The patients presented with early onset, progressive and different severities with CORD. CONCLUSION This is the first report of the clinical phenotype of CRX mutation (p.R41W) in Chinese families, and the mutation can lead to a wide range of various retinal phenotypes.
Journal Title: International journal of ophthalmology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!