Photo from wikipedia
In this editorial, we discuss recent evidence from our research group on the analgesic and antiinflammatory mechanisms of the flavonoid naringenin (4’,5,7-tryhidroxy-flavanone). Flavonoids are polyphenolic compounds found in human diet… Click to show full abstract
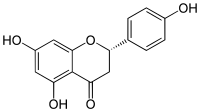
In this editorial, we discuss recent evidence from our research group on the analgesic and antiinflammatory mechanisms of the flavonoid naringenin (4’,5,7-tryhidroxy-flavanone). Flavonoids are polyphenolic compounds found in human diet [1]. Naringenin belongs to flavanone class of flavonoids, and it is mainly found in citrus fruits including, lemon, orange, tangerine and grapefruit [1-5]. The antioxidant activity is the most recognized effect of flavonoids, which depends, for instance, on hydrogen donation and electron stabilization in the phenolic rings [1]. Naringenin presents therapeutic effect in several models of inflammatory pain [2, 3, 5]. Naringenin inhibits the pain-like behavior induced by inflammatory stimuli such as phenyl-p-benzoquinone, acetic acid, formalin, complete Freund ́s adjuvant, capsaicin, carrageenan [2], superoxide anion [3], and LPS [5]. Moreover, naringenin inhibits UVB irradiation-induced skin inflammatory edema, cytokine production, myeloperoxidase activity, matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity, and oxidative stress [4]. Pathogen (PAMPs) and damage (DAMPs) associated molecular patterns and inflammatory mediators activate resident macrophages. Resident macrophages produce chemotactic molecules to recruit leukocytes to the inflammatory foci, mainly neutrophils in the early events of inflammation. Activated macrophages and neutrophils induce oxidative stress by producing superoxide anion and other reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen species. Naringenin inhibits leukocyte recruitment [2-5] and production of superoxide anion [3-5], whilst increases GSH [2-4], and antioxidant capacity [3-5]. Naringenin also acts on macrophages inducing Nrf2 activation, a nuclear factor that induces antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses, inducing HO-1 expression [3]. PAMPs, DAMPs and ROS induce NFκB activation in macrophages resulting in the production of pro-hyperalgesic cytokine such as IL-33, TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6. Pro-hyperalgesic cytokines induce the production of lipid mediators such as PGE2 that sensitize the nociceptor neurons. Naringenin inhibits LPSand carrageenan-induced NFκB activation in vivo [2] and in vitro [5], which contributes to naringenin inhibition of IL-33 [2], TNFα [3-5], IL-1β [2, 4, 5] and IL-6 [4,5] production and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA [3] (Figure 1).
Journal Title: Oncotarget
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!