Photo from wikipedia
Nature is always the best inspiration for basic research. A family with severe thrombosis and antithrombin deficiency, the strongest anticoagulant, carried a new mutation affecting the translation-start codon of SERPINC1,… Click to show full abstract
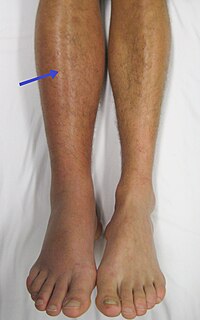
Nature is always the best inspiration for basic research. A family with severe thrombosis and antithrombin deficiency, the strongest anticoagulant, carried a new mutation affecting the translation-start codon of SERPINC1, the gene encoding antithrombin. Expression of this variant in a eukaryotic cell system produced three different antithrombins. Two downstream methionines were used as alternative initiation codons, generating highly expressed small aglycosylated antithrombins with cytoplasmic localization. Wild-type antithrombin was generated by the use of the mutated AUU as initiation codon. Actually, any codon except for the three stop codons might be used to initiate translation in this strong Kozak context. We show unexpected consequences of natural mutations affecting translation-start codons. Downstream alternative initiation AUG codons may be used when the start codon is mutated, generating smaller molecules with potential different cell localization, biochemical features and unexplored consequences. Additionally, our data further support the use of other codons apart from AUG for initiation of translation in eukaryotes.
Journal Title: Oncotarget
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!