Photo from wikipedia
» Spondylolysis is defined as a defect of the pars interarticularis, and spondylolisthesis is defined as a slippage of a vertebra relative to the immediately caudal vertebra. » Most cases… Click to show full abstract
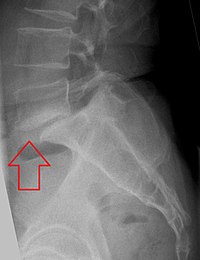
» Spondylolysis is defined as a defect of the pars interarticularis, and spondylolisthesis is defined as a slippage of a vertebra relative to the immediately caudal vertebra. » Most cases of spondylolysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis can be treated nonoperatively. Depending on a patient's age, nonoperative treatment may include a thoracolumbosacral orthosis (TLSO), physical therapy, and activity modification. Bracing and physical therapy have been found to be more effective than activity modification alone. » Patients with dysplastic spondylolisthesis are at higher risk for progression and should be monitored with serial radiographs every 6 to 9 months. » Operative management is recommended for symptomatic patients with failure of at least 6 months of nonoperative management or patients with high-grade spondylolisthesis. » Surgical techniques include pars defect repair, reduction, and fusion, which may include posterior-only, anterior-only, or circumferential fusion.
Journal Title: JBJS reviews
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!