Photo from wikipedia
Capacitance-to-Digital Converter (CDC) ICs available in the market use square wave excitation signals but a sinusoidal excitation is preferred in various applications, such as ice detection, liquid level measurement, humidity… Click to show full abstract
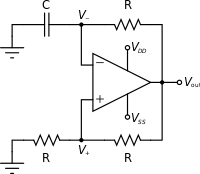
Capacitance-to-Digital Converter (CDC) ICs available in the market use square wave excitation signals but a sinusoidal excitation is preferred in various applications, such as ice detection, liquid level measurement, humidity measurement, proximity sensing, etc. A dual slope technique based CDC that employs a sinusoidal excitation has been reported recently, but it requires a large number of excitation cycles, to complete an accurate conversion. This paper presents an improved CDC that employs a specially designed method to achieve high accuracy even when a much smaller number of excitation cycles, than the reported scheme, are employed to complete the conversion. A prototype CDC has been developed and tested. In comparison with an existing CDC, the new CDC achieved a substantial reduction (by a factor of 4000) in the number of excitation cycles during integration period, resulting in an improved update rate. Worst case error observed from the prototype CDC was less than 0.24%. Keywords-capacitance-to-digital converter; sinusoidal excitation; conversion rate; accuracy; capacitive sensor.
Journal Title: International Journal on Smart Sensing and Intelligent Systems
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!