Photo from wikipedia
BACKGROUND Large animal fracture models that allow for anatomic fracture fixation are currently lacking. It was hypothesized that a compressed air impaction system can generate a reproducible tibial plafond fracture… Click to show full abstract
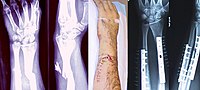
BACKGROUND Large animal fracture models that allow for anatomic fracture fixation are currently lacking. It was hypothesized that a compressed air impaction system can generate a reproducible tibial plafond fracture and be adjustable to create fractures consistent with high and low energy fractures seen in humans. METHODS Pilot testing of the impaction system was done by impacting polyurethane foam blocks at varying compressed air pressures. A guillotine impaction test was performed on the same foam blocks to create an energy conversion. A total of 12 porcine hindlimb hindlimbs were subjected to low-energy (42.2 J) and high-energy (73.9 J) impact to create tibial plafond fractures. FINDINGS Guillotine impaction test demonstrated strong correlations between potential energy and foam block impaction depth (R2 = 0.99). Compressed air impaction system test strongly correlated with foam block impaction depth (R2 = 0.99). All six porcine hindlimbs in the low-energy group developed simple coronal split tibial plafond fractures. All six porcine hindlimbs in the high-energy group developed complex, multi-fragmentary tibial plafond fractures. INTERPRETATION This porcine fracture model created tibial plafond fracture patterns with similar fracture morphology as human patients without violation of the soft tissue structures or adjacent joints. This model would allow for anatomic fixation, the study of post-traumatic osteoarthritis, or the delivery of locally targeted therapeutics to the ankle joint.
Journal Title: Clinical biomechanics
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!