Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Advances in molecular biology and neuroscience have led to the discovery of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a 37 amino-acid neuropeptide that plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of… Click to show full abstract
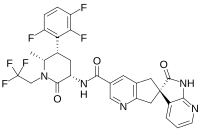
Abstract Advances in molecular biology and neuroscience have led to the discovery of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a 37 amino-acid neuropeptide that plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of migraine. CGRP receptor antagonist, also known as gepant, is an oral medication that inhibits the CGRP-related nociceptive signaling pathway. To date, three gepants are approved by the FDA for migraine treatment. Atogepant is a 2nd-generation gepant that non-competitively antagonizes CGRP receptors inhibiting neurogenic inflammation and pain sensitization. With its long half-life and minimal cardiovascular or liver toxicity, it is the first in its class approved primarily for migraine prevention. This article will discuss the evidence, safety, and rationale of atogepant for use in clinical practice.
Journal Title: Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!