Photo from wikipedia
This paper presents a machine learning approach for classification of arsenic (As) levels as safe and unsafe in groundwater samples collected from the Indo-Gangetic region. As water is essential for… Click to show full abstract
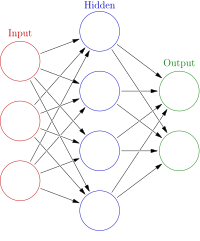
This paper presents a machine learning approach for classification of arsenic (As) levels as safe and unsafe in groundwater samples collected from the Indo-Gangetic region. As water is essential for sustaining life, heavy metals like arsenic pose a public health concern. In this study, various tree-based machine learning models namely Random Forest, Optimized Forest, CS Forest, SPAARC, and REP Tree algorithms have been applied to classify water samples. As per the guidelines of the World Health Organization (WHO), the arsenic concentration in water should not exceed 10 μg/L. The groundwater quality parameter was ranked using a classifier attribute evaluator for training and testing the models. Parameters obtained from the confusion matrix, such as accuracy, precision, recall, and FPR, were used to analyze the performance of models. Among all models, Optimized Forest outperforms other classifier as it has a high accuracy of 80.64%, a precision of 80.70%, recall of 97.87%, and a low FPR of 73.33%. The Optimized Forest model can be used to test new water samples for classification of arsenic in groundwater samples.
Journal Title: Journal of water and health
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!