Photo from wikipedia
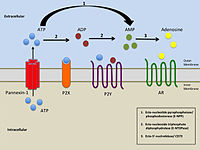
The purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-gated cation channel protein. Although extracellular ATP (eATP) is maintained at the nanomolar concentration range under normal conditions, it is elevated… Click to show full abstract
The purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-gated cation channel protein. Although extracellular ATP (eATP) is maintained at the nanomolar concentration range under normal conditions, it is elevated to micromolar levels in response to cell stress or damage, resulting in activation of P2X7R in the brain. Binding of eATP to P2X7R in glial cells in the brain activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and releases proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18 and TNFα. Depression has been demonstrated to be strongly associated with neuroinflammation activated by P2X7R. Therefore, P2X7R is an attractive therapeutic target for depression. Multi-national pharmaceutical companies, including AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Pfizer, have developed CNS-penetrating P2RX7 antagonists. Several of these have been evaluated in clinical trials. This review summarizes the recent development of P2X7R antagonists as novel antidepressant agents in terms of structural optimization, as well as in vitro/in vivo evaluation and physicochemical properties of representative compounds.
Journal Title: Current medicinal chemistry
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!