Photo from wikipedia
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Fetal MR imaging is part of the comprehensive prenatal assessment of fetuses with open spinal dysraphism. We aimed to assess the reliability of brain stem and posterior… Click to show full abstract
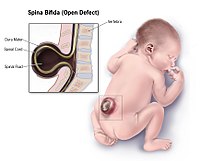
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Fetal MR imaging is part of the comprehensive prenatal assessment of fetuses with open spinal dysraphism. We aimed to assess the reliability of brain stem and posterior fossa measurements; use the reliable measurements to characterize fetuses with open spinal dysraphism versus what can be observed in healthy age-matched controls; and document changes in those within 1 week after prenatal repair. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Retrospective evaluation of 349 MR imaging examinations took place, including 274 in controls and 52 in fetuses with open spinal dysraphism, of whom 23 underwent prenatal repair and had additional early postoperative MR images. We evaluated measurements of the brain stem and the posterior fossa and the ventricular width in all populations for their reliability and differences between the groups. RESULTS: The transverse cerebellar diameter, cerebellar herniation level, clivus-supraocciput angle, transverse diameter of the posterior fossa, posterior fossa area, and ventricular width showed an acceptable intra- and interobserver reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient > 0.5). In fetuses with open spinal dysraphism, these measurements were significantly different from those of healthy fetuses (all with P < .0001). Furthermore, they also changed significantly (P value range = .01 to < .0001) within 1 week after the fetal operation with an evolution toward normal, most evident for the clivus-supraocciput angle (65.9 ± 12.5°; 76.6 ± 10.9; P < .0001) and cerebellar herniation level (−9.9 ± 4.2 mm; −0.7 ± 5.2; P < .0001). CONCLUSIONS: In fetuses with open spinal dysraphism, brain stem measurements varied substantially between observers. However, measurements characterizing the posterior fossa could be reliably assessed and were significantly different from normal. Following a fetal operation, these deviations from normal values changed significantly within 1 week.
Journal Title: American Journal of Neuroradiology
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!