Photo from wikipedia
Randomized clinical trials have evaluated the role of anticoagulants in the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in ambulatory cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. This meta-analysis is aimed at providing an… Click to show full abstract
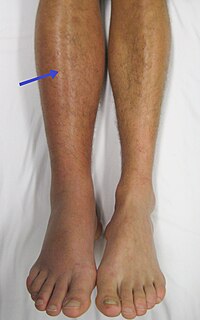
Randomized clinical trials have evaluated the role of anticoagulants in the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in ambulatory cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. This meta-analysis is aimed at providing an updated evaluation of the efficacy and safety of anticoagulant prophylaxis in this clinical setting. Medline and Scopus were searched to retrieve randomized controlled trials on the prevention of VTE in ambulatory cancer patients. Two groups of trials were identified with VTE or death as the primary outcome, respectively. VTE was the primary outcome of this analysis. Anticoagulant prophylaxis reduced the incidence of VTE in studies in which the primary outcome was VTE [14 studies, 8,226 patients; odds ratio (OR)=0.45; 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 0.36-0.56] or death (8 studies, 3,727 patients; OR=0.61; 95% CI: 0.47-0.81). When these studies were pooled together, VTE was reduced by 49% (95% CI: 0.43-0.61) with no significant increase in major bleeding (OR=1.30, 95% CI: 0.98-1.73). The risk of major bleeding was increased in studies with VTE as the primary outcome (OR=1.43, 95% CI: 1.01-2.04). Similar reductions of VTE were observed in studies with parenteral (OR=0.43, 95% CI: 0.33-0.56) or oral anticoagulants (OR=0.49, 95% CI: 0.33-0.74). The reduction in VTE was confirmed in patients with lung (OR=0.42, 95% CI: 0.26-0.67) or pancreatic cancer (OR=0.26, 95% CI: 0.14-0.48), in estimated high-risk patients, in high-quality studies and with respect to symptomatic VTE. In conclusion, prophylaxis with oral or parenteral anticoagulants reduces the risk of VTE in ambulatory cancer patients, with an acceptable increase in major bleeding.
Journal Title: Haematologica
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!