Photo from wikipedia
Heart diseases are leading cause of death around the world. Given their unique capacity to self-renew and differentiate into all types of somatic cells, human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) hold… Click to show full abstract
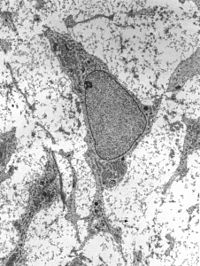
Heart diseases are leading cause of death around the world. Given their unique capacity to self-renew and differentiate into all types of somatic cells, human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) hold great promise for heart disease modeling and cardiotoxic drug screening. hPSC-derived cardiac organoids are emerging biomimetic models for studying heart development and cardiovascular diseases, but it remains challenging to make mature organoids with a native-like structure in vitro. In this study, temporal modulation of Wnt signaling pathway co-differentiated hPSCs into beating cardiomyocytes and cardiac endothelial-like cells in 3D organoids, resulting in cardiac endothelial-bounded chamber formation. These chambered cardiac organoids exhibited more mature membrane potential compared to cardiac organoids composed of only cardiomyocytes. Furthermore, a better response to toxic drugs was observed in chamber-contained cardiac organoids. In summary, spatiotemporal signaling pathway modulation may lead to more mature cardiac organoids for studying cardiovascular development and diseases.
Journal Title: Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!