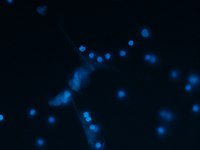
Photo from wikipedia
NETs are chromatin-derived webs extruded from neutrophils as a result of either infection or sterile stimulation using chemicals, cytokines, or microbes. In addition to the classical role that NETs play… Click to show full abstract
NETs are chromatin-derived webs extruded from neutrophils as a result of either infection or sterile stimulation using chemicals, cytokines, or microbes. In addition to the classical role that NETs play in innate immunity against infection and injuries, NETs have been implicated extensively in cancer progression, metastatic dissemination, and therapy resistance. The purpose of this review is to describe recent investigations into NETs and the roles they play in tumor biology and to explore their potential as therapeutic targets in cancer treatment.
Journal Title: Frontiers in Immunology
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!