Photo from wikipedia
Background White matter hyperintensities (WMH) are a key imaging feature of cerebral small-vessel disease (CSVD). However, there is a lack of standardized methods for determining WMH volume, and the value… Click to show full abstract
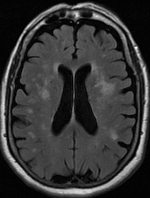
Background White matter hyperintensities (WMH) are a key imaging feature of cerebral small-vessel disease (CSVD). However, there is a lack of standardized methods for determining WMH volume, and the value of total white matter (WM) volume in the assessment of cognitive impairment in patients with CSVD remains unknown. Objective We aimed to explore the correlations of WMH volume and WM volume with cognitive dysfunction and its components in patients with CSVD. We also aimed to compare the value of the Fazekas score, WMH volume, and ratio of WMH volume to total WM volume in the assessment of cognitive dysfunction. Methods The study included 99 patients with CSVD. Patients were categorized into following groups based on MoCA scores: patients with mild cognitive impairment and those without. Brain magnetic resonance images were processed to investigate differences in WMH and WM volumes between the groups. Logistic regression analysis was used to determine whether these two factors were independent risk factors for cognitive dysfunction. Correlation analysis was used to examine the relationships of WMH and WM volume with different types of cognitive impairment. Receiver operating characteristic curves were used to compare the effectiveness of the WMH score, WMH volume, and WMH to WM ratio for evaluating cognitive dysfunction. Results There were significant differences in age, education level, WMH volume, and WM volume between the groups (P < 0.05). After adjusting for age and education, the multivariate logistic analysis indicated that both WMH volume and WM volume were independent risk factors for cognitive dysfunction. Correlation analysis indicated that WMH volume was mainly related to cognition involving the visual space and delayed recall. WM volume was not strongly associated with different types of cognitive dysfunction. The WMH to WM ratio was the strongest predictor, with an area under the curve value of 0.800 and a 95% confidence interval of 0.710–0.891. Conclusion Increases in WMH volume may aggravate cognitive dysfunction in patients with CSVD, and a higher WM volume may reduce the effect of WMH volume on cognitive function to a certain extent. The ratio of WMH to total WM volume may reduce the impact of brain atrophy, allowing for more accurate evaluation of cognitive dysfunction in older adults with CSVD.
Journal Title: Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!