Photo from wikipedia
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) mediate intercellular communication by transferring genetic material, proteins and organelles between different cells types in both health and disease. Recent evidence suggests that these vesicles, more than… Click to show full abstract
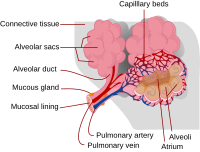
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) mediate intercellular communication by transferring genetic material, proteins and organelles between different cells types in both health and disease. Recent evidence suggests that these vesicles, more than simply diagnostic markers, are key mediators of the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and other lung diseases. In this review, we will discuss the contribution of EVs released by pulmonary structural cells (alveolar epithelial and endothelial cells) and immune cells in these diseases, with particular attention to their ability to modulate inflammation and alveolar-capillary barrier disruption, a hallmark of ARDS. EVs also offer a unique opportunity to develop new therapeutics for the treatment of ARDS. Evidences supporting the ability of stem cell-derived EVs to attenuate the lung injury and ongoing strategies to improve their therapeutic potential are also discussed.
Journal Title: Frontiers in Physiology
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!