Photo from wikipedia
Background: Intubation of a patient in different positions may be done not only in emergency settings, but also in routine anesthesia (e.g., prone position for lumbar spine surgery). Methods: The… Click to show full abstract
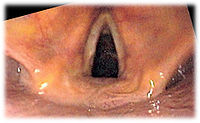
Background: Intubation of a patient in different positions may be done not only in emergency settings, but also in routine anesthesia (e.g., prone position for lumbar spine surgery). Methods: The aim of the study was to compare the classic Macintosh blade laryngoscope with two videolaryngoscopes: the Pentax-AWS and the Intubrite in a simulated scenario of a manikin placed in a sitting and prone position. Additionally, intubation with the use of all three devices was performed in a standard supine position as the control group. The time of intubation and the pressure exerted on the tongue was assessed. The ANOVA Friedman (analysis of variance) and Wilcoxon with Bonferroni correction tests were used for statistical analysis. Results: The time of intubation in a prone position was significantly shorter for the Pentax-AWS videolaryngoscope compared to the Macintosh and the Intubrite. There were no significant differences in the obtained results of the evaluated devices in sitting and standard positions. The lowest pressure exerted on the tongue was with the Pentax-AWS, followed by the Intubrite and the Macintosh laryngoscopes. Conclusions: The use of the Pentax-AWS was associated with faster tracheal intubation, creating lower pressure on tongue when compared with standard Macintosh and Intubrite laryngoscopes in both prone and sitting positions.
Journal Title: Diagnostics
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!