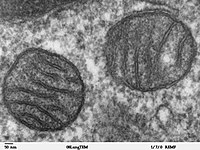
Photo from wikipedia
Mitochondria supply cells with energy in the form of ATP, guide apoptosis, and contribute to calcium buffering and reactive oxygen species production. To support these diverse functions, mitochondria form an… Click to show full abstract
Mitochondria supply cells with energy in the form of ATP, guide apoptosis, and contribute to calcium buffering and reactive oxygen species production. To support these diverse functions, mitochondria form an extensive network with smaller clusters that are able to move along microtubules aided by motor proteins. Mitochondria are also associated with the actin network, which is involved in cellular responses to various mechanical factors. In this review, we discuss mitochondrial structure and function in relation to the cytoskeleton and various mechanical factors influencing cell functions. We first summarize the morphological features of mitochondria with an emphasis on fission and fusion as well as how network properties govern function. We then review the relationship between the mitochondria and the cytoskeletal structures, including mechanical interactions. We also discuss how stretch and its dynamic pattern affect mitochondrial structure and function. Finally, we present preliminary data on how extracellular matrix stiffness influences mitochondrial morphology and ATP generation. We conclude by discussing the more general role that mitochondria may play in mechanobiology and how the mechanosensitivity of mitochondria may contribute to the development of several diseases and aging.
Journal Title: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!