Photo from wikipedia
In cystic fibrosis (CF), impaired airway surface hydration (ASL) and mucociliary clearance that promote chronic bacterial colonization, persistent inflammation, and progressive structural damage to the airway wall architecture are typically… Click to show full abstract
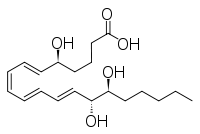
In cystic fibrosis (CF), impaired airway surface hydration (ASL) and mucociliary clearance that promote chronic bacterial colonization, persistent inflammation, and progressive structural damage to the airway wall architecture are typically explained by ion transport abnormalities related to the mutation of the gene coding for the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) channel. However, the progressive and unrelenting inflammation of the CF airway begins early in life, becomes persistent, and is excessive relative to the bacterial burden. Intrinsic abnormalities of the inflammatory response in cystic fibrosis have been suggested but the mechanisms involved remain poorly understood. This review aims to give an overview of the recent advances in the understanding of the defective resolution of inflammation in CF including the abnormal production of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (lipoxin and resolvin) and their impact on the pathogenesis of the CF airway disease.
Journal Title: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!