Photo from wikipedia
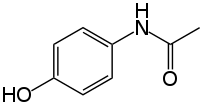
The mechanism of acetaminophen (APAP) analgesia is at least partially unknown. Previously, we showed that the APAP metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) activated Kv7 channels in neurons in vitro, and this… Click to show full abstract
The mechanism of acetaminophen (APAP) analgesia is at least partially unknown. Previously, we showed that the APAP metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) activated Kv7 channels in neurons in vitro, and this activation of Kv7 channels dampened neuronal firing. Here, the effect of the Kv7 channel blocker XE991 on APAP-induced analgesia was investigated in vivo. APAP had no effect on naive animals. Induction of inflammation with λ-carrageenan lowered mechanical and thermal thresholds. Systemic treatment with APAP reduced mechanical hyperalgesia, and co-application of XE991 reduced APAP’s analgesic effect on mechanical pain. In a second experiment, the analgesic effect of systemic APAP was not antagonized by intrathecal XE991 application. Analysis of liver samples revealed APAP and glutathione-coupled APAP indicative of metabolization. However, there were no relevant levels of these metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid, suggesting no relevant APAP metabolite formation in the CNS. In summary, the results support an analgesic action of APAP by activating Kv7 channels at a peripheral site through formation of the metabolite NAPQI.
Journal Title: International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!