Photo from wikipedia
Simple Summary Mosquitoes transmit disease, and over the past century, mosquito control has mostly relied on chemical insecticides that target the adult life stage. We review methods of mosquito control… Click to show full abstract
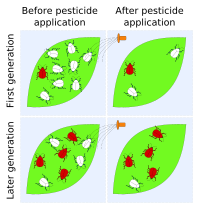
Simple Summary Mosquitoes transmit disease, and over the past century, mosquito control has mostly relied on chemical insecticides that target the adult life stage. We review methods of mosquito control and argue that photoactive molecules that target larvae—called photosensitive insecticides or PSIs—are an environmentally friendly addition to our mosquitocidal arsenal. Abstract Insecticides reduce the spread of mosquito-borne disease. Over the past century, mosquito control has mostly relied on neurotoxic chemicals—such as pyrethroids, neonicotinoids, chlorinated hydrocarbons, carbamates and organophosphates—that target adults. However, their persistent use has selected for insecticide resistance. This has led to the application of progressively higher amounts of insecticides—known as the pesticide treadmill—and negative consequences for ecosystems. Comparatively less attention has been paid to larvae, even though larval death eliminates a mosquito’s potential to transmit disease and reproduce. Larvae have been targeted by source reduction, biological control, growth regulators and neurotoxins, but hurdles remain. Here, we review methods of mosquito control and argue that photoactive molecules that target larvae—called photosensitive insecticides or PSIs—are an environmentally friendly addition to our mosquitocidal arsenal. PSIs are ingested by larvae and produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) when activated by light. ROS then damage macromolecules resulting in larval death. PSIs are degraded by light, eliminating environmental accumulation. Moreover, PSIs only harm small translucent organisms, and their broad mechanism of action that relies on oxidative damage means that resistance is less likely to evolve. Therefore, PSIs are a promising alternative for controlling mosquitoes in an environmentally sustainable manner.
Journal Title: Insects
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!