Photo from wikipedia
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a rare disease that affects connective tissue, which causes abnormalities in several organ systems including the heart, eyes, bones, and joints. The autosomal dominant disorder was… Click to show full abstract
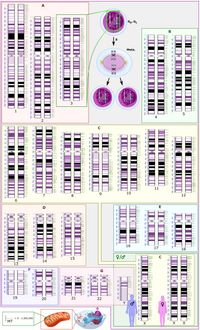
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a rare disease that affects connective tissue, which causes abnormalities in several organ systems including the heart, eyes, bones, and joints. The autosomal dominant disorder was found to be strongly associated with FBN1, TGFBR1, and TGFBR2 mutations. Although multiple genetic mutations have been reported, data from Asian populations are still limited. As a result, we utilized the whole exome sequencing (WES) technique to identify potential pathogenic variants of MFS in a Taiwan cohort. In addition, a variety of annotation databases were applied to identify the biological functions as well as the potential mechanisms of candidate genes. In this study, we confirmed the pathogenicity of FBN1 to MFS. Our results indicated that TTN and POMT1 may be likely related to MFS phenotypes. Furthermore, we found nine unique variants highly shared in a MFS family cohort, of which eight are novel variants worthy of further investigation.
Journal Title: Journal of Personalized Medicine
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!