Photo from wikipedia
The straight groove test of AZ31B magnesium alloy sheet by electric hot temperature-controlled incremental sheet forming (ISF) was conducted at different temperatures. The temperature influence on fracture depth, deformation force… Click to show full abstract
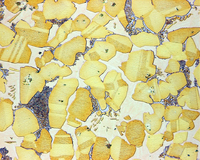
The straight groove test of AZ31B magnesium alloy sheet by electric hot temperature-controlled incremental sheet forming (ISF) was conducted at different temperatures. The temperature influence on fracture depth, deformation force and strain distribution was investigated. It was found that the limit depth and major strain increased as the temperature rose and that the forming force decreased correspondingly. Furthermore, the fracture behavior changed from brittle fracture to ductile fracture. Considering the formability and surface wear comprehensively, the optimized forming temperature was determined to be 300 °C. The microstructure of the groove specimen was analyzed and the dynamic recrystallization (DRX) was considered to be the reason for the improved formability. The degree of DRX depended on the temperature and degree of deformation, which resulted in non-uniform distribution of hardness within the cross section of the groove specimen.
Journal Title: Materials
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!