Photo from wikipedia
Plant-derived products have been used since the beginnings of human history to treat various pathological conditions. Practical experience as well as a growing body of research suggests the benefits of… Click to show full abstract
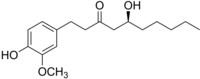
Plant-derived products have been used since the beginnings of human history to treat various pathological conditions. Practical experience as well as a growing body of research suggests the benefits of the use of turmeric (Curcuma longa) and some of its active components in the reduction of oxidative stress, a mechanism leading to neurodegeneration. In this current study, we investigated the effects of a preparation of Curcuma longa, and its constituents curcumin, tetrahydrocurcumin, and curcumenol, in one of the molecular pathways leading to oxidative stress, which is the release of NO, a free radical involved in stress conditions, using the BV2 microglial cell line. The concentration-dependent reduction of NO is linked to reduced amounts of iNOS protein- and mRNA-synthesis and is possibly mediated by the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) such as p42/44 or p38 MAPK. Therefore, the use of turmeric extract is a promising therapeutic option for diseases linked to the dysregulation of oxidative stress, with fewer side-effects in comparison to the currently used pharmacotherapeutics.
Journal Title: Molecules
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!