Photo from wikipedia
Ecolabeling can complement more conventional policy instruments such as taxes and subsidies to stimulate more sustainable development of the economy. However, in practice, ecolabels may not always comply with legal… Click to show full abstract
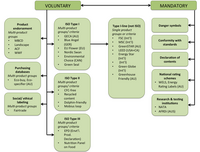
Ecolabeling can complement more conventional policy instruments such as taxes and subsidies to stimulate more sustainable development of the economy. However, in practice, ecolabels may not always comply with legal requirements in terms of reliability, accuracy and clarity, and sometimes deliberately mislead the consumer. In Russia and many other developing countries, the problem of inaccurate information on the environmental properties of goods and services is still not recognized. The only regulatory document that currently defines the basic principles for developing and using environmental labels and declarations is the national versions of international standards ISO 14020/14021/14024/14025-Environmental Labels Package. This paper contributes to the literature in two main dimensions. It assesses the degree of prevalence of ecolabeling in the Russian market of everyday goods and the reliability and informational content of frequently used labels (supply-side research). Second, it estimates the consumers’ awareness and reaction to ecolabeled products (demand-side research). The most obvious finding to emerge from this study is that low consumer awareness keeps the level of greenwashing low, but at the same time does not stimulate eco-innovations. We suggest developing smartphone applications that allow buyers to check the compliance of ecolabels on a product with ISO standards directly during the shopping process. We propose to use this approach as a cost-effective and straightforward way to simultaneously raise consumer awareness of ecolabeling and reduce the likelihood of greenwashing.
Journal Title: Sustainability
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!