Photo from wikipedia
As part of an effort to engineer ricin antitoxins and immunotherapies, we previously produced and characterized a collection of phage-displayed, heavy chain-only antibodies (VHHs) from alpacas that had been immunized… Click to show full abstract
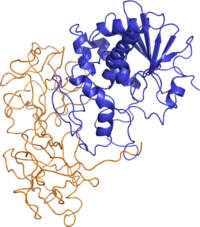
As part of an effort to engineer ricin antitoxins and immunotherapies, we previously produced and characterized a collection of phage-displayed, heavy chain-only antibodies (VHHs) from alpacas that had been immunized with ricin antigens. In our initial screens, we identified nine VHHs directed against ricin toxin’s binding subunit (RTB), but only one, JIZ-B7, had toxin-neutralizing activity. Linking JIZ-B7 to different VHHs against ricin’s enzymatic subunit (RTA) resulted in several bispecific antibodies with potent toxin-neutralizing activity in vitro and in vivo. JIZ-B7 may therefore be an integral component of a future VHH-based neutralizing agent (VNA) for ricin toxin. In this study, we now localize, using competitive ELISA, JIZ-B7’s epitope to a region of RTB’s domain 2 sandwiched between the high-affinity galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine (Gal/GalNAc)-binding site and the boundary of a neutralizing hotspot on RTA known as cluster II. Analysis of additional RTB (n = 8)- and holotoxin (n = 4)-specific VHHs from a recent series of screens identified a “supercluster” of neutralizing epitopes at the RTA-RTB interface. Among the VHHs tested, toxin-neutralizing activity was most closely associated with epitope proximity to RTA, and not interference with RTB’s ability to engage Gal/GalNAc receptors. We conclude that JIZ-B7 is representative of a larger group of potent toxin-neutralizing antibodies, possibly including many described in the literature dating back several decades, that recognize tertiary and possibly quaternary epitopes located at the RTA-RTB interface and that target a region of vulnerability on ricin toxin.
Journal Title: Toxins
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!